About The Author: Travis Baugh is a Digital Brand Marketing Manager for Bryant, where he creates clear, helpful content to guide homeowners through heating, cooling, and indoor air quality decisions. His goal is to empower readers with the knowledge they need to choose the right comfort solutions for their home—confidently and comfortably.
What Is EER vs. EER2? Energy Efficiency Ratio Explained
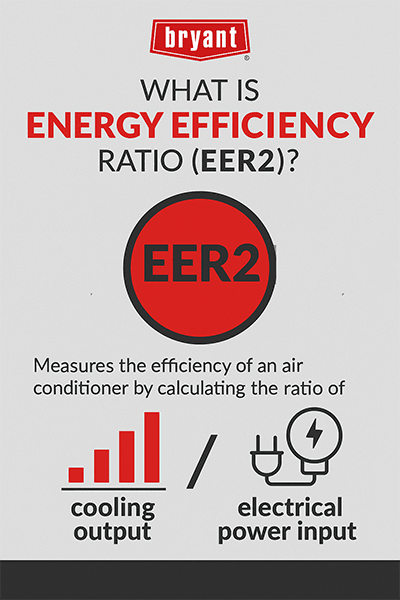
EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) measures an air conditioner’s cooling efficiency at a specific outdoor temperature (typically 95°F). It is calculated by dividing the unit's cooling output (in BTUs) by its electrical input (in watts). EER2 is the updated 2023 standard that accounts for higher external static pressure, providing a more accurate reflection of real-world energy performance.
How EER and EER2 Work
When you shop for a new air conditioner or heat pump you’ll see efficiency ratings that tell you how much energy the system uses to keep your home cool. The higher the rating, the more efficient the unit—and the lower your potential electricity bills.
EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio)
EER is a snapshot of efficiency. Unlike SEER2 (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), which averages performance over an entire cooling season, EER tests the unit under peak conditions: 95°F outdoor temperature, 80°F indoor temperature, and 50% relative humidity. This makes
EER an excellent metric for homeowners in consistently hot climates where air conditioning systems run at maximum capacity often.
EER2 (The New Standard)
Introduced in 2023, EER2 updates the testing procedure to better simulate installed conditions. It accounts for the energy required to push air through ductwork (external static pressure). Because this test is more rigorous, EER2 ratings typically appear slightly lower than legacy EER ratings for the exact same equipment, but they are far more accurate for predicting actual energy usage.
The Difference Between SEER2 and EER2
While both metrics measure efficiency, they serve different purposes:
- SEER2 (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio 2): Measures efficiency over a typical cooling season, accounting for varied temperatures. It’s like "highway miles per gallon" for your AC—great for varied climates.
- EER2 (Energy Efficiency Ratio 2): Measures efficiency at peak load (high heat). It’s like "city miles per gallon" in heavy traffic. If you live in a region with sustained high temperatures, EER2 is often a more critical number to watch.
David Fowler, owner of Family Heating and Air in Pensacola, Florida, stresses the importance of considering EER2 when purchasing a central air conditioner.
“EER2 is measured under peak load rather than a seasonal load,” Fowler said. “This allows homeowners to know that their unit will maintain the efficiency it was designed for, even when it’s really hot outside.”
What Is a Good EER2 Rating?
Generally, an EER2 rating of 10 to 12 or higher is considered efficient for modern air conditioners. The most advanced systems can reach even higher numbers.
- Standard Efficiency: EER2 ~ 9.0 – 10.0
- High Efficiency: EER2 ~ 11.0 – 12.5+
Investing in a higher EER2 unit often results in lower monthly utility bills, especially during heat waves. While high-efficiency units may have a higher upfront cost, the long-term energy savings—combined with available rebates —can offer significant value.
“The higher the EER, the less electricity the unit uses, which translates to lower electricity bills,” Mark Lea, co-owner of Lea Heating & Air Conditioning in East Dundee, IL, said. “I like to compare it to miles per gallon on a car — would you buy a car without considering its MPG?”
Benefits of High EER2 Systems
Choosing a system with a high EER2 rating offers tangible benefits beyond just a lower electric bill.
- Peak Performance: These systems are engineered to handle the hottest days of the year without struggling, maintaining consistent comfort.
- Environmental Impact: Consuming less electricity reduces your carbon footprint, contributing to a more sustainable future.
- Enhanced Comfort: High-efficiency units often come with advanced features like variable-speed compressors, which provide better humidity control and quieter operation.
How to Choose the Right EER2 for Your Home
Selecting the right rating isn't just about getting the highest number possible; it's about matching the system to your specific needs.
- Check Your Climate: If you live in the South or Southwest, prioritize a high EER2 rating because your split AC unit will frequently operate at peak temperatures. In milder northern climates, a standard EER2 might suffice.
- Calculate Long-Term Value: Compare the upfront cost difference against potential energy savings over the system's 15–20 year lifespan.
- Consult an Expert: A local Bryant dealer can perform a load calculation and recommend the specific efficiency sweet spot for your home’s layout and insulation.
FAQs on EER
EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) measures an air conditioner’s cooling efficiency at a specific outdoor temperature (usually 95°F), showing how much cooling output you get per unit of energy used. EER2 (Energy Efficiency Ratio 2) is the updated version of EER, reflecting newer testing standards introduced in 2023 that better simulate real-world conditions, including increased external static pressure.
A good EER2 rating for an air conditioner is generally around 10.0 or higher, with higher numbers indicating better energy efficiency under the updated testing conditions.
EER2 is the updated version of the Energy Efficiency Ratio that measures how efficiently an HVAC system uses energy under specific test conditions.
It represents the cooling output of an air conditioner divided by the power it consumes, giving a clearer picture of energy efficiency than the old EER standard.
EER2 is important because a higher rating means better efficiency, which can help lower cooling bills and improve long-term performance.
The EER2 value is a number assigned to the unit—higher numbers indicate more efficient air conditioners.
EER2 ratings are typically lower because the testing conditions are harder. The new standards account for the energy required to push air through ductwork, which wasn't fully factored into the old EER calculation.
No, the minimum required EER2 ratings often differ between split system air conditioners and packaged units. Split systems generally require higher ratings to meet regional efficiency standards.
Learn More About Air Conditioners
- Learn how does air conditioning work
- Get in the know on air conditioning service
- Find out what is a and an inverter air conditioner
- Understand AC maintenance and AC tune ups
- Discover the factors in choosing the and what size air conditioner you need


